), abbreviated detergent guide, Calbiochem, Commonly used detergents, Frost lecture, UFL, Wikipedia: Critical micelle concentration, Explanation and Video showing an educational experiment to determine the CMC of SDS, Uni Wisconsin, https://openwetware.org/mediawiki/index.php?title=Critical_micelle_concentration_(CMC)&oldid=1080646. What is the aggregation number in chemistry? Below the CMC the surface tension decreases with increasing surfactant concentration as the number of surfactants at the interface increases. The study of the aggregation of lipids (amphiphiles) is known as lipid polymorphism, and forms part of current academic research. Your browser does not support JavaScript. in surface tension measurements or conductivity measurements, the amount of surfactant at the interface is negligible compared to that in the bulk and CMC is approximated by the total concentration as is done in most of the textbooks.

Moreover, varying parameters like temperature or system composition micelles can also adopt forms other than spherical, such as elongated and worm-like structures. Any further addition of surfactants will lead to the formation of micelles. Note: Saponin is a class of amphiphilic, natural metabolites with detergent properties often extracted from plants.
Definitions.net.
Mater. [5] J. Kim, D. Lee, H. Shum, & D. Weitz, "Colloid Surfactants for Emulsion Stabilization," Adv. [1] R. Jones, "Soft Condensed Matter," Oxford University Press Inc., New York (2002).
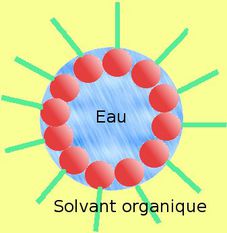
CMC is an important characteristic of a surfactant. Critical micelle concentration (CMC) is defined as the concentration of detergents above which micelles are spontaneously formed. Knowing the CMC can help develop a product with certain characteristics. The critical micelle concentration CMC is the surfactant concentration at and above which micelles are formed. In the paper Colloid Surfactants for Emulsion Stabilization, the authors observe clusters of amphiphilic particles analogous to micelles of surfactant molecules. The polar part of the molecule can interact strongly with polar solvents, like water, and is therefore also called the hydrophilic part. Wikipedia article "Critical_micelle_concentration". The concentration at which an amphipathic molecule (e.g., a phospholipid) will form a micelle. At this concentration the surface-area between two liquids is fully loaded with surfactants and there is no room for additional ones. This page has been accessed 16,360 times. In liquid crystals also layered structures are found. Micelles only form above critical micelle temperature. An extrapolation of respective regression lines yields the CMC at the intersection. The word BULK is important because surfactants partition between the bulk and interface and CMC is independent of interface and is therefore a characteristic of the surfactant molecule.
There are several theoretical definitions of CMC. How do you do ion exchange chromatography? There may be an occasional micelle formed below the CMC. The non-polar part, on the other hand, can form strong interactions with non-polar solvents, like oil, and is therefore also called lipophilic or hydrophobic part. However, above the CMC, the vast majority of added surfactant will form micelles. Similar reasoning holds for emulsions. https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/critical+micelle+concentration. Do amphiphilic particles also obey a critical aggregation concentration? The Critical Micelle Concentration (CMC) is the concentration of surfactants in a solution above which micelles form. At a water surface, for example, the surfactants orient themselves in such a way that the head group resides in the water and the hydrocarbon chain points to the gaseous phase (see figure 2). To use all functions of this page, please activate cookies in your browser. In chemistry, we look at the law of mass action to see how much of a reactant (in this case, individual surfactants) will form a product (in this case, micelles). This page was last edited on 9 April 2020, at 06:54. In colloidal and surface chemistry, the critical micelle concentration is defined as the concentration of surfactants above which micelles form and all additional surfactants added to the system go to micelles.
Read what you need to know about our industry portal chemeurope.com. The CMC is an important characteristic of a surfactant. Below the CMC, almost no micelles form, while above it, lots of micelles form. [3] I. Morrison, "Surfactant Phases," http://soft-matter.seas.harvard.edu/index.php/Surfactant_phases. Removal of oily soil is by modification of the contact angles and release of oil in the form of emulsion. Find out how LUMITOS supports you with online marketing. To use all the functions on Chemie.DE please activate JavaScript. [2] T. Witten, "Structured Fluids: Polymers, Colloids, Surfactants," Oxford University Press Inc., New York (2004).

How to say critical micelle concentration in sign language? Surfactants adsorb preferably at interfaces where they find the energetically most favorable conditions due to their two-part structure. However, once micelles form localized pockets of hydrophobic tails, the dye moves from the paper into the centers of the micelles which are free to float about the container. All content on this website, including dictionary, thesaurus, literature, geography, and other reference data is for informational purposes only. There are important situations where interfacial areas are large and the amount of surfactant at the interface can not be neglected. The Critical Micelle Concentration is related to the law of mass action [2]. They consist of a polar head group and a non-polar hydrocarbon chain (see figure 1).
micelle schematic petrographic surfactant lawsonia lawsone The critical micelle concentration is the point of surfactant concentration at which micelles form and all additional added surfactants go to micelles.
Surfactants can be classified according to the charge of their polar head group: Figure 1: Schematic structure of a surfactant. On the other hand, when the degree of aggregation is multidispersion, CMC is related to both the method of measurement and the dispersion. Below this borderline, detergents merely partition into membranes without solubilising membrane proteins. In addition to the micelles shown in figure 3 so-called inverse micelles exist which cluster their head groups and orient their chains towards a surrounding non-polar phase. Surfactants are interfacially active compounds. For example, the value of CMC for sodium dodecyl sulfate in water at 25 C, atmospheric pressure, is 8x10-3 mol/L. For example micelles form which consist of several clustered surfactant molecules that shield their non-polar chains from the surrounding aqueous phase with their polar head groups (see figure 3). Above the CMC, in contrast, the surface tension of the solution is constant because the interfacial surfactant concentration does not change any more. When the degree of aggregation is monodispersion, the CMC is not related to the method of measurement. Once the interface (and the adjacent volume phases) are saturated the addition of more surfactants will not decrease the interfacial tension any further (see figure 4). CMC is the concentration of surfactants in the bulk at which micelles start forming. Thus surfactants can mediate between two phases as they can form strong interactions with both of them. What are the differences between calcium ion indicators: Cal 520, Cal 520FF, and Cal 520N?
http://www.mrsec.wisc.edu/Edetc/nanolab/micelle. This is one of the easiest methods to remove surfactants from effluents ( Foam Flotation)!!. translations for critical micelle concentration, critical micelle concentration definitions, https://www.definitions.net/definition/critical+micelle+concentration. CMC may vary. Colloid Surfactants for Emulsion Stabilization, http://soft-matter.seas.harvard.edu/index.php/Surfactant_phases, http://www.mrsec.wisc.edu/Edetc/nanolab/micelle, http://soft-matter.seas.harvard.edu/index.php?title=Critical_Micelle_Concentration&oldid=11327. After reaching the CMC, the surface tension remains relatively constant or changes with a lower slope. Critical micelle concentration (CMC) and surfactant concentration. Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 does not support some functions on Chemie.DE. adsorption capacity (mol/[m.sup.2]) [infinity]] [[GAMMA].sub.m] minimum value of the surfactant concentration at the barrier ring required to prevent coalescence (mol/[m.sup.2]) [mu] viscosity of the medium (Pa s) [rho] density of the liquid phase (kg/[m.sub.3]) [[lambda].sub.i] zeros of the Bessel function of the first kind and order one ([J.sub.1]) [[sigma].sub. [4] J. Breitzer, M. Lye, & G. Lisensky, "Critical Micelle Concentration," University of Wisconsin, Madision, Materials Research Science and Engineering Center (July 11, 2008). We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly. After reaching the CMC, the surface tensions stays more constant. STANDS4 LLC, 2022. Copyright 2021 AAT Bioquest, Inc. All Rights Reserved. The decrease of the interfacial tension caused by surfactants becomes stronger the more surfactants are adsorbed at the interface. One well-known definition is that CMC is the total concentration of surfactants under the conditions: Therefore, CMC depends on the method of measuring the samples, since a and b depend on the properties of the solution such as conductance and photochemical characteristics.
micelles crosslinked rsc tem surface rgd polyurea conjugated peptide polymerization raft core via For example if we take a solution of a surfactant above CMC and start introducing air bubbles at the bottom of the solution, these bubbles, as they rise to the surface, pull out the surfactants from the bulk to the top of the solution creating a foam column thus bringing down the concentration in bulk to below cmc.
 Moreover, varying parameters like temperature or system composition micelles can also adopt forms other than spherical, such as elongated and worm-like structures. Any further addition of surfactants will lead to the formation of micelles. Note: Saponin is a class of amphiphilic, natural metabolites with detergent properties often extracted from plants. Definitions.net. Mater. [5] J. Kim, D. Lee, H. Shum, & D. Weitz, "Colloid Surfactants for Emulsion Stabilization," Adv. [1] R. Jones, "Soft Condensed Matter," Oxford University Press Inc., New York (2002).
Moreover, varying parameters like temperature or system composition micelles can also adopt forms other than spherical, such as elongated and worm-like structures. Any further addition of surfactants will lead to the formation of micelles. Note: Saponin is a class of amphiphilic, natural metabolites with detergent properties often extracted from plants. Definitions.net. Mater. [5] J. Kim, D. Lee, H. Shum, & D. Weitz, "Colloid Surfactants for Emulsion Stabilization," Adv. [1] R. Jones, "Soft Condensed Matter," Oxford University Press Inc., New York (2002).  CMC is an important characteristic of a surfactant. Critical micelle concentration (CMC) is defined as the concentration of detergents above which micelles are spontaneously formed. Knowing the CMC can help develop a product with certain characteristics. The critical micelle concentration CMC is the surfactant concentration at and above which micelles are formed. In the paper Colloid Surfactants for Emulsion Stabilization, the authors observe clusters of amphiphilic particles analogous to micelles of surfactant molecules. The polar part of the molecule can interact strongly with polar solvents, like water, and is therefore also called the hydrophilic part. Wikipedia article "Critical_micelle_concentration". The concentration at which an amphipathic molecule (e.g., a phospholipid) will form a micelle. At this concentration the surface-area between two liquids is fully loaded with surfactants and there is no room for additional ones. This page has been accessed 16,360 times. In liquid crystals also layered structures are found. Micelles only form above critical micelle temperature. An extrapolation of respective regression lines yields the CMC at the intersection. The word BULK is important because surfactants partition between the bulk and interface and CMC is independent of interface and is therefore a characteristic of the surfactant molecule. There are several theoretical definitions of CMC. How do you do ion exchange chromatography? There may be an occasional micelle formed below the CMC. The non-polar part, on the other hand, can form strong interactions with non-polar solvents, like oil, and is therefore also called lipophilic or hydrophobic part. However, above the CMC, the vast majority of added surfactant will form micelles. Similar reasoning holds for emulsions. https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/critical+micelle+concentration. Do amphiphilic particles also obey a critical aggregation concentration? The Critical Micelle Concentration (CMC) is the concentration of surfactants in a solution above which micelles form. At a water surface, for example, the surfactants orient themselves in such a way that the head group resides in the water and the hydrocarbon chain points to the gaseous phase (see figure 2). To use all functions of this page, please activate cookies in your browser. In chemistry, we look at the law of mass action to see how much of a reactant (in this case, individual surfactants) will form a product (in this case, micelles). This page was last edited on 9 April 2020, at 06:54. In colloidal and surface chemistry, the critical micelle concentration is defined as the concentration of surfactants above which micelles form and all additional surfactants added to the system go to micelles. Read what you need to know about our industry portal chemeurope.com. The CMC is an important characteristic of a surfactant. Below the CMC, almost no micelles form, while above it, lots of micelles form. [3] I. Morrison, "Surfactant Phases," http://soft-matter.seas.harvard.edu/index.php/Surfactant_phases. Removal of oily soil is by modification of the contact angles and release of oil in the form of emulsion. Find out how LUMITOS supports you with online marketing. To use all the functions on Chemie.DE please activate JavaScript. [2] T. Witten, "Structured Fluids: Polymers, Colloids, Surfactants," Oxford University Press Inc., New York (2004).
CMC is an important characteristic of a surfactant. Critical micelle concentration (CMC) is defined as the concentration of detergents above which micelles are spontaneously formed. Knowing the CMC can help develop a product with certain characteristics. The critical micelle concentration CMC is the surfactant concentration at and above which micelles are formed. In the paper Colloid Surfactants for Emulsion Stabilization, the authors observe clusters of amphiphilic particles analogous to micelles of surfactant molecules. The polar part of the molecule can interact strongly with polar solvents, like water, and is therefore also called the hydrophilic part. Wikipedia article "Critical_micelle_concentration". The concentration at which an amphipathic molecule (e.g., a phospholipid) will form a micelle. At this concentration the surface-area between two liquids is fully loaded with surfactants and there is no room for additional ones. This page has been accessed 16,360 times. In liquid crystals also layered structures are found. Micelles only form above critical micelle temperature. An extrapolation of respective regression lines yields the CMC at the intersection. The word BULK is important because surfactants partition between the bulk and interface and CMC is independent of interface and is therefore a characteristic of the surfactant molecule. There are several theoretical definitions of CMC. How do you do ion exchange chromatography? There may be an occasional micelle formed below the CMC. The non-polar part, on the other hand, can form strong interactions with non-polar solvents, like oil, and is therefore also called lipophilic or hydrophobic part. However, above the CMC, the vast majority of added surfactant will form micelles. Similar reasoning holds for emulsions. https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/critical+micelle+concentration. Do amphiphilic particles also obey a critical aggregation concentration? The Critical Micelle Concentration (CMC) is the concentration of surfactants in a solution above which micelles form. At a water surface, for example, the surfactants orient themselves in such a way that the head group resides in the water and the hydrocarbon chain points to the gaseous phase (see figure 2). To use all functions of this page, please activate cookies in your browser. In chemistry, we look at the law of mass action to see how much of a reactant (in this case, individual surfactants) will form a product (in this case, micelles). This page was last edited on 9 April 2020, at 06:54. In colloidal and surface chemistry, the critical micelle concentration is defined as the concentration of surfactants above which micelles form and all additional surfactants added to the system go to micelles. Read what you need to know about our industry portal chemeurope.com. The CMC is an important characteristic of a surfactant. Below the CMC, almost no micelles form, while above it, lots of micelles form. [3] I. Morrison, "Surfactant Phases," http://soft-matter.seas.harvard.edu/index.php/Surfactant_phases. Removal of oily soil is by modification of the contact angles and release of oil in the form of emulsion. Find out how LUMITOS supports you with online marketing. To use all the functions on Chemie.DE please activate JavaScript. [2] T. Witten, "Structured Fluids: Polymers, Colloids, Surfactants," Oxford University Press Inc., New York (2004).  How to say critical micelle concentration in sign language? Surfactants adsorb preferably at interfaces where they find the energetically most favorable conditions due to their two-part structure. However, once micelles form localized pockets of hydrophobic tails, the dye moves from the paper into the centers of the micelles which are free to float about the container. All content on this website, including dictionary, thesaurus, literature, geography, and other reference data is for informational purposes only. There are important situations where interfacial areas are large and the amount of surfactant at the interface can not be neglected. The Critical Micelle Concentration is related to the law of mass action [2]. They consist of a polar head group and a non-polar hydrocarbon chain (see figure 1). micelle schematic petrographic surfactant lawsonia lawsone The critical micelle concentration is the point of surfactant concentration at which micelles form and all additional added surfactants go to micelles. Surfactants can be classified according to the charge of their polar head group: Figure 1: Schematic structure of a surfactant. On the other hand, when the degree of aggregation is multidispersion, CMC is related to both the method of measurement and the dispersion. Below this borderline, detergents merely partition into membranes without solubilising membrane proteins. In addition to the micelles shown in figure 3 so-called inverse micelles exist which cluster their head groups and orient their chains towards a surrounding non-polar phase. Surfactants are interfacially active compounds. For example, the value of CMC for sodium dodecyl sulfate in water at 25 C, atmospheric pressure, is 8x10-3 mol/L. For example micelles form which consist of several clustered surfactant molecules that shield their non-polar chains from the surrounding aqueous phase with their polar head groups (see figure 3). Above the CMC, in contrast, the surface tension of the solution is constant because the interfacial surfactant concentration does not change any more. When the degree of aggregation is monodispersion, the CMC is not related to the method of measurement. Once the interface (and the adjacent volume phases) are saturated the addition of more surfactants will not decrease the interfacial tension any further (see figure 4). CMC is the concentration of surfactants in the bulk at which micelles start forming. Thus surfactants can mediate between two phases as they can form strong interactions with both of them. What are the differences between calcium ion indicators: Cal 520, Cal 520FF, and Cal 520N?
How to say critical micelle concentration in sign language? Surfactants adsorb preferably at interfaces where they find the energetically most favorable conditions due to their two-part structure. However, once micelles form localized pockets of hydrophobic tails, the dye moves from the paper into the centers of the micelles which are free to float about the container. All content on this website, including dictionary, thesaurus, literature, geography, and other reference data is for informational purposes only. There are important situations where interfacial areas are large and the amount of surfactant at the interface can not be neglected. The Critical Micelle Concentration is related to the law of mass action [2]. They consist of a polar head group and a non-polar hydrocarbon chain (see figure 1). micelle schematic petrographic surfactant lawsonia lawsone The critical micelle concentration is the point of surfactant concentration at which micelles form and all additional added surfactants go to micelles. Surfactants can be classified according to the charge of their polar head group: Figure 1: Schematic structure of a surfactant. On the other hand, when the degree of aggregation is multidispersion, CMC is related to both the method of measurement and the dispersion. Below this borderline, detergents merely partition into membranes without solubilising membrane proteins. In addition to the micelles shown in figure 3 so-called inverse micelles exist which cluster their head groups and orient their chains towards a surrounding non-polar phase. Surfactants are interfacially active compounds. For example, the value of CMC for sodium dodecyl sulfate in water at 25 C, atmospheric pressure, is 8x10-3 mol/L. For example micelles form which consist of several clustered surfactant molecules that shield their non-polar chains from the surrounding aqueous phase with their polar head groups (see figure 3). Above the CMC, in contrast, the surface tension of the solution is constant because the interfacial surfactant concentration does not change any more. When the degree of aggregation is monodispersion, the CMC is not related to the method of measurement. Once the interface (and the adjacent volume phases) are saturated the addition of more surfactants will not decrease the interfacial tension any further (see figure 4). CMC is the concentration of surfactants in the bulk at which micelles start forming. Thus surfactants can mediate between two phases as they can form strong interactions with both of them. What are the differences between calcium ion indicators: Cal 520, Cal 520FF, and Cal 520N?  http://www.mrsec.wisc.edu/Edetc/nanolab/micelle. This is one of the easiest methods to remove surfactants from effluents ( Foam Flotation)!!. translations for critical micelle concentration, critical micelle concentration definitions, https://www.definitions.net/definition/critical+micelle+concentration. CMC may vary. Colloid Surfactants for Emulsion Stabilization, http://soft-matter.seas.harvard.edu/index.php/Surfactant_phases, http://www.mrsec.wisc.edu/Edetc/nanolab/micelle, http://soft-matter.seas.harvard.edu/index.php?title=Critical_Micelle_Concentration&oldid=11327. After reaching the CMC, the surface tension remains relatively constant or changes with a lower slope. Critical micelle concentration (CMC) and surfactant concentration. Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 does not support some functions on Chemie.DE. adsorption capacity (mol/[m.sup.2]) [infinity]] [[GAMMA].sub.m] minimum value of the surfactant concentration at the barrier ring required to prevent coalescence (mol/[m.sup.2]) [mu] viscosity of the medium (Pa s) [rho] density of the liquid phase (kg/[m.sub.3]) [[lambda].sub.i] zeros of the Bessel function of the first kind and order one ([J.sub.1]) [[sigma].sub. [4] J. Breitzer, M. Lye, & G. Lisensky, "Critical Micelle Concentration," University of Wisconsin, Madision, Materials Research Science and Engineering Center (July 11, 2008). We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly. After reaching the CMC, the surface tensions stays more constant. STANDS4 LLC, 2022. Copyright 2021 AAT Bioquest, Inc. All Rights Reserved. The decrease of the interfacial tension caused by surfactants becomes stronger the more surfactants are adsorbed at the interface. One well-known definition is that CMC is the total concentration of surfactants under the conditions: Therefore, CMC depends on the method of measuring the samples, since a and b depend on the properties of the solution such as conductance and photochemical characteristics. micelles crosslinked rsc tem surface rgd polyurea conjugated peptide polymerization raft core via For example if we take a solution of a surfactant above CMC and start introducing air bubbles at the bottom of the solution, these bubbles, as they rise to the surface, pull out the surfactants from the bulk to the top of the solution creating a foam column thus bringing down the concentration in bulk to below cmc.
http://www.mrsec.wisc.edu/Edetc/nanolab/micelle. This is one of the easiest methods to remove surfactants from effluents ( Foam Flotation)!!. translations for critical micelle concentration, critical micelle concentration definitions, https://www.definitions.net/definition/critical+micelle+concentration. CMC may vary. Colloid Surfactants for Emulsion Stabilization, http://soft-matter.seas.harvard.edu/index.php/Surfactant_phases, http://www.mrsec.wisc.edu/Edetc/nanolab/micelle, http://soft-matter.seas.harvard.edu/index.php?title=Critical_Micelle_Concentration&oldid=11327. After reaching the CMC, the surface tension remains relatively constant or changes with a lower slope. Critical micelle concentration (CMC) and surfactant concentration. Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 does not support some functions on Chemie.DE. adsorption capacity (mol/[m.sup.2]) [infinity]] [[GAMMA].sub.m] minimum value of the surfactant concentration at the barrier ring required to prevent coalescence (mol/[m.sup.2]) [mu] viscosity of the medium (Pa s) [rho] density of the liquid phase (kg/[m.sub.3]) [[lambda].sub.i] zeros of the Bessel function of the first kind and order one ([J.sub.1]) [[sigma].sub. [4] J. Breitzer, M. Lye, & G. Lisensky, "Critical Micelle Concentration," University of Wisconsin, Madision, Materials Research Science and Engineering Center (July 11, 2008). We're doing our best to make sure our content is useful, accurate and safe.If by any chance you spot an inappropriate comment while navigating through our website please use this form to let us know, and we'll take care of it shortly. After reaching the CMC, the surface tensions stays more constant. STANDS4 LLC, 2022. Copyright 2021 AAT Bioquest, Inc. All Rights Reserved. The decrease of the interfacial tension caused by surfactants becomes stronger the more surfactants are adsorbed at the interface. One well-known definition is that CMC is the total concentration of surfactants under the conditions: Therefore, CMC depends on the method of measuring the samples, since a and b depend on the properties of the solution such as conductance and photochemical characteristics. micelles crosslinked rsc tem surface rgd polyurea conjugated peptide polymerization raft core via For example if we take a solution of a surfactant above CMC and start introducing air bubbles at the bottom of the solution, these bubbles, as they rise to the surface, pull out the surfactants from the bulk to the top of the solution creating a foam column thus bringing down the concentration in bulk to below cmc.